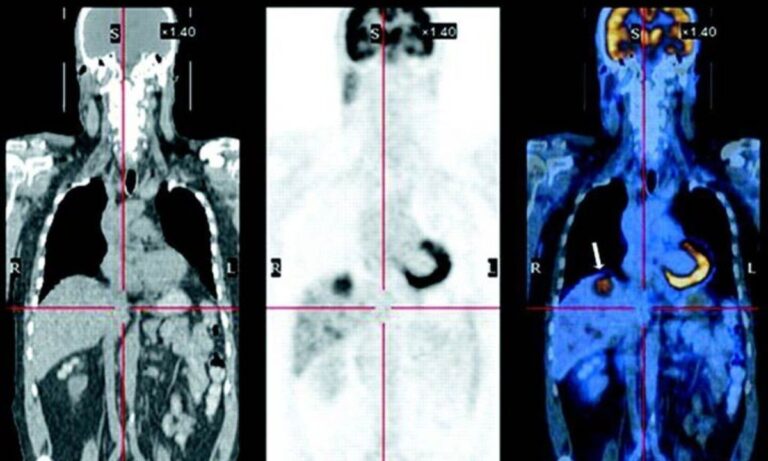
Medical imaging technologies like CT scans and PET scans are invaluable in modern healthcare. They play a significant role in diagnosing various conditions, understanding the progress of diseases, and planning treatments. While both are crucial diagnostic tools,
They differ significantly in terms of their principles, procedures, and applications. In this article, we will explore the differences between a CT scan and a PET scan, comparing their advantages and disadvantages, as well as their roles in diagnosing health conditions.
What is a CT Scan?
A CT scan (or Computed Tomography scan) uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. It combines multiple X-ray images taken from different angles and uses computer processing to create images
That are more detailed than regular X-rays. CT scans can be used for a wide variety of medical conditions, including trauma, infections, tumors, and internal bleeding.
How CT Scans Work
During the procedure, the patient lies down on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The X-ray beam rotates around the body,
And detectors capture the X-rays that pass through, creating slices or sections of the body. These slices are then compiled into a detailed image by a computer.
Advantages of a CT Scan
- Fast and Non-invasive: CT scans are quick procedures, typically taking only a few minutes. They are non-invasive, meaning they don’t require surgical incisions.
- Detailed Images: CT scans provide high-resolution images that can help detect problems such as tumors, internal bleeding, or bone fractures.
- Wide Applications: CT scans are used to examine a variety of conditions, from injuries to diagnosing cancer, and even evaluating heart disease.
Disadvantages of a CT Scan
- Radiation Exposure: One of the major disadvantages of CT scans is the exposure to X-ray radiation, which may increase the risk of cancer over time, especially with frequent use.
- Limited Soft Tissue Detail: Although CT scans are excellent at showing bone and hard tissue structures, they may not provide as much detail for soft tissues like the brain or muscles.
Read This Blog; Can You Have a Pet Capybara in Australia?
What is a PET Scan?
A PET scan or Positron Emission Tomography scan) is a type of nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces 3D images of the functional processes inside the body. It works by detecting
The radiation emitted by small amounts of radioactive material, often a form of glucose, which is injected into the body before the scan. Cells in the body absorb the glucose, and the PET scan detects where this glucose is metabolized.
How PET Scans Work
During a PET scan, a small amount of radioactive substance (usually a form of glucose) is injected into the patient’s vein. The substance collects in the organs and tissues, and the scanner detects the radiation emitted.
The resulting images reveal how the organs and tissues are functioning rather than just their structure.
Advantages of a PET Scan
- Functional Imaging: PET scans provide functional images, meaning they show how the body’s tissues and organs are working, not just their structure.
- Cancer Detection: PET scans are particularly useful in detecting cancer as tumors often have high metabolic activity and absorb more glucose than normal tissues.
- Early Detection: PET scans can detect changes in the body before anatomical changes occur, which is helpful in detecting diseases early on.
Disadvantages of a PET Scan
- Radiation Exposure: Like CT scans, PET scans also involve exposure to radioactive material, though the dose is typically low.
- Expensive: PET scans are usually more expensive than CT scans and are not as widely available. They may also require specialized facilities.
- Time-Consuming: The PET scan procedure can take longer than a CT scan, typically requiring 30 minutes to an hour.
Differences Between a CT Scan and a PET Scan
Although both CT scans and PET scans are crucial for diagnosing various health conditions, their purposes and applications differ significantly. Below is a comparison of the two:
| Feature | CT Scan | PET Scan |
| Technology | Uses X-rays to create detailed images of body structures | Uses radioactive tracers to show functional activity in tissues |
| Best for | Detecting structural issues like fractures, tumors, and infections | Diagnosing cancer, heart disease, and brain disorders |
| Image Type | Provides detailed structural images | Provides functional and metabolic images |
| Radiation | Yes, exposes the body to X-rays | Yes, exposes the body to radioactive tracers |
| Duration | Quick (a few minutes) | Longer (30-60 minutes) |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | More expensive and less widely available |
| Frequency | Can be performed more frequently | Limited in frequency due to radiation exposure |
| Availability | Widely available in hospitals and clinics | More specialized, available in fewer locations |
CT Scan Vs. PET Scan: What’s the Difference?
A CT scan is more focused on providing detailed structural images. It uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the body, helping doctors assess bones, soft tissues, and blood vessels.
CT scans are often the first imaging choice when looking for trauma, internal bleeding, or cancer. It’s great for understanding anatomy and identifying physical changes in the body’s structure.
CT and Cancer
CT scans are helpful in identifying cancerous tumors and determining their size and location. They can also be used for staging cancer, showing whether the cancer has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
However, CT scans are less effective in evaluating the functional aspect of cancer cells compared to PET scans.
Read This Blog; Why Do Dogs Yawn When You Pet Them?
Positron Emission Tomography
A PET scan, on the other hand, allows doctors to evaluate tissue function. This scan is particularly useful for detecting cancer because cancer cells often have a higher rate of glucose metabolism compared to normal cells.
A PET scan can reveal metabolic activity, allowing doctors to detect small tumors that may not show up on a CT scan.
Which is More Accurate A PET Scan or CT Scan?
The accuracy of a PET scan or CT scan depends on the situation. CT scans are better for providing detailed anatomical images, especially for identifying bone fractures, internal bleeding, or large tumors.
However, PET scans are better for identifying metabolic activity and functional changes in the body’s tissues, making them especially useful in cancer diagnosis. In some cases, CT and PET scans are used together for more accurate diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a CT scan detect cancer?
Yes, CT scans can detect cancerous tumors and show their size and location.
Is a PET scan used for cancer detection?
Yes, PET scans are primarily used for detecting cancer as they can show areas of high metabolic activity, typical of tumors.
How long does a PET scan take?
A PET scan typically takes around 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the procedure.
Which is more expensive, CT scan or PET scan?
Generally, PET scans are more expensive than CT scans, mainly due to the use of radioactive tracers and the specialized equipment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both CT scans and PET scans are essential tools in modern medicine, each offering unique benefits. CT scans excel in providing detailed structural images of the body, making them perfect for diagnosing injuries, infections, and structural abnormalities. PET scans, on the other hand, are invaluable for understanding the functional aspects of diseases, particularly cancer.
Understanding when to use each imaging technique—and in some cases, combining them—can greatly enhance the accuracy of diagnoses and the effectiveness of treatment plans. Whether you’re seeking answers to structural or functional concerns, both types of scans offer crucial insights for healthcare providers.